Plaster types: what is plaster
Types of plasters are quite different. These mixtures are used for leveling surfaces and protecting building envelopes from various negative environmental influences.
Today we will consider the types of facade plaster, get acquainted with their characteristics and the possibility of application. Also on the video in this article you can get a lot of additional and necessary information.
The content of the article
Choose plaster material
Types and purpose of plaster can be divided into two main types.
They are excellent in fraction and in characteristics:
| For exterior surfaces | This option has a large fraction and is intended for decoration of external surfaces. It tolerates moisture and temperature extremes. |
| For interior work | This type has a small fraction. With its help it is quite possible to make a smooth and even surface. But he is not resistant to external influences. |
Purpose and types of plaster are also divided according to their functionality.
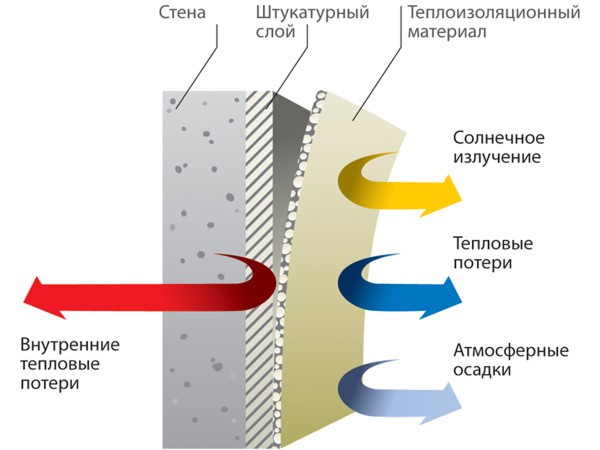
Heat protection
It is also called “warm” (seeWarm plaster: composition and features of use), it is used in the decoration of facades and interior buildings to increase their thermal properties.
- The basis of this plaster is a cement-sand mortar. The introduction of insulating fillers into its composition: perlite sand, vermiculite, polystyrene foam, granulated foam glass, qualitatively changes the properties of the solution.
- All ingredients are quite light in weight, have a low density. When surface finishing with plasters containing these materials, it is possible to reduce the load on the foundation.
- In addition, with such a finish, it is completely possible to abandon the external insulation from mineral wool boards or expanded polystyrene.
- This type of plaster involves not only heat-shielding properties. It incorporates mineral fillers, which classify it as a class of non-combustible materials (with the exception of the composition with expanded polystyrene).
Acoustic
This plaster provides sound insulation in the production halls of industrial enterprises, it is used to reduce noise in offices of public buildings, restaurants, cafes.
Attention: It is often used in the decoration of residential premises to reduce noise, plastering walls and floors.
- Acoustic plaster is based on cement or gypsum. Its fillers can be crushed slag pumice, expanded clay, vermiculite or volcanic glass, which give it sound-absorbing properties due to its relatively low density.
- To increase sound absorption, aluminum powder is added to the mixture, which makes the plaster more porous. The applied solution should not be overwritten so that the voids in the filler are not clogged with the base.
- Acoustic plaster can be applied to any substrate that has been previously primed with a cement-sand mortar (1: 2) with the addition of lime (10%).
- It is undesirable to paint or whitewash this type of plaster, as this reduces the level of sound absorption.
Waterproofing
New types of high-density plaster are used to form the coating and at the same time smooth the surface of the structure.
So:
- The composition of the plaster mixtures contains water repellents, thanks to which the material does not absorb water, making the coating completely waterproof.
- Most often they contain polymers - epoxy, acrylic and polyurethane resins. Such coverage must be arranged in fountains, pools, cellars, basements, partially or fully buried in the ground. It protects structures from the penetration of groundwater, high humidity, and withstands the pressure of a column of water 5 meters high.
- Two types of waterproofing plasters have found application: cement-sand and asphalt. In the production of cement-sand plasters, aluminosilicates, finely divided ground coal and stone flour, bitumen, etc. are used as sealing additives.
- Mixtures necessarily contain plasticizers: adisol-mylonaphth, ordinary sodium oleate or sodium palmitate, which give it hydrophobic characteristics. There is a mechanized way to protect structures - layer-by-layer gunning under pressure using a cement gun.
- Asphalt plaster is widely used in waterproofing building elements. The composition of hot plaster includes bitumen of road grades, polymer additives (crumb rubber, latex), fillers and sand. Before applying it, it is necessary to prepare the base: make a notch, clean, dry, prime.
- Asphalt plaster can be applied manually and using asphalt grinder, which greatly speeds up the plastering process. Cold asphalt plaster is a lime-bitumen paste with the addition of Portland cement, latex, and brick powder. The mixture is applied in layers from the bottom up. To protect against mechanical damage, the plaster is fenced with cement screed, panel formwork, etc.
Special plaster
Plaster types are also of a special orientation. Its price is much higher than the sweat of ordinary material. This surface treatment is used for highly specialized purposes when some specific protective properties are required from the room: from X-rays or from the influence of external aggressive conditions (acids, etc.).
It is usually used in the decoration of industrial buildings, medical facilities and chemical laboratories. When designing a construction object, those premises that should be finished with special solutions are determined in advance. The drawings indicate the names of the compositions and the area of plastering, the amount of materials used, and in the estimates all necessary expenses are laid.
Views:
- X-ray protective plaster mixused in rooms with sources of ionizing radiation. Its main filler is ground barite concentrate (barium sulfate). The thickness of the plaster layer is previously calculated in the laboratory, it must correspond to the degree of radiation of the installations. Application barite plaster more economical than finishing with lead screens, so it is widespread. Work is carried out at a temperature of + 15-20 ° C, and normal humidity. If the layer thickness exceeds 30 mm, then the plaster layer is applied on a mesh fixed to the base. With an estimated thickness of more than 50 mm, it is more advisable to use barite plates as a finish.
- Acid resistant plaster most often used in the decoration of buildings and structures operated under the influence of gaseous aggressive environments. In its composition, it has a complex combination of quartz sand (as a filler), water glass (potassium or sodium), acid-resistant cement, and sodium silicofluoride hardener for hardening the solution. From above, the surface of acid-resistant plaster is covered with a cement-sand mortar. This will protect the layer from the destructive effect of air.
- Fireproof plaster resistant to temperatures up to + 200 ° C, it is able to contain a fire for two hours.Heat-resistant flame retardant plaster mixture is used for finishing internal surfaces at enterprises where combustible materials and high temperatures are used, for finishing furnaces in industrial production, as well as home fireplaces. It is able to minimize fire damage and has recently been often used in the decoration of private houses, baths, saunas. Refractory plaster mix is made on the basis of kaolin clay, fireclay dust and water glass. It is necessary to apply the plaster on a dust-free, solvent-free, primed base, or by using a cement gun. The main thing when working with such material is that the finished solution is worked out within 30 minutes, and the strips deposited on the surface overlap each other to avoid the appearance of seams.
Attention: When buying special plasters, the instructions should be studied. After all, it is not always possible to apply it with your own hands, and her specialization is rather narrow.
Decorative
At the heart of decorative (seeWhat types of decorative plaster exist) plasters are used cement-lime, silicate, silicone and polymer compositions. As a filler there are various additives in the form of mica, stone chips, fragments of shell rock, wood fibers.
It happens:
- Structural (with inclusions) (cm.Structural plaster: application technology);
- Textured (to create a relief on the surface);
- Flock (liquid wallpaper);
- Marble (with granite and marble inclusions);
- Venetian (cm. Venetian plaster: features of the use of material), (from fine marble flour, to create a surface resembling a slice of marble or malachite).
The list of its advantages can be made:
- Suitable for coloring;
- It is durable and strong, resistant to cracking;
- Hides all surface imperfections (bumps, small cracks);
- Frost-resistant, has good soundproofing properties, some of its types are waterproof;
- Suitable for application on any surface (metal, concrete, brick, wood);
- For any design project of the room, you can choose a composition that is able to emphasize the chosen style;
- Eco-friendly, does not emit toxic substances.
There are not many disadvantages:
- Such plaster is difficult to dismantle;
- At the cost of the compositions and the cost of applying them, it is more expensive than other finishing materials;
- It is applied only to a thoroughly cleaned, pre-primed surface.
Decorative plastering of facades and interior spaces dramatically changes the whole look of the building, adding sophistication and completeness to the style decision.
Types of plasters by composition
Plaster types can be different in composition. Each is suitable for its type of work.
Plain
According to the method of application, conventional plaster is distinguished for facade and for internal work.
- The solutions used for outdoor use have hydrophobicity, frost resistance, and UV resistance. Their use as a finish depends on the material of the enclosing structures. Plaster mortar should have the ability to work on the surface, filling all the bumps.
- For cellular concrete with high vapor permeability, gypsum-based mixtures with various additives are most often used. Aerated concrete, foam concrete, gas silicate differ in their structure, therefore, the approach to their decoration is also not the same, specialist consultation is required.
Plastering the walls indoors is done with water-based solutions. Plaster is simple, improved and high quality. Distinguishing between them is quite simple.
Walls of non-residential and auxiliary premises are covered with ordinary plaster, often it is the basis for ceramic tiles, or is covered with other finishing materials.At the same time, peeling of plaster, cracks, sinks, efflorescences, traces of trowel tools are not allowed on the surface.
- Improved (for facades) plaster is used in residential and public buildings. More stringent requirements apply to it in terms of vertical and horizontal deviations (which should be less than 2 mm), the number of bumps on the surface, and gaps. All these norms are taken into account by SNiP. Checking the quality of work is carried out by special devices: rule, plumb line and probe. Flatness of the surface is measured on an area of 10 square meters. m in three places.
- High-quality (indoors) plaster is made using a beacon. It is applied in several stages: spraying, priming, and a thin (about 2 mm) top coat. Depending on the degree of surface roughness, the number of layers may be greater. This perfect alignment is used if no further trim is provided. High-quality plaster is quite expensive in connection with a longer and better work process.
All of the above plasters are wet or monolithic plasters. Their versatility, plasticity, hiding power, lack of seams allows you to apply on any complex contour surfaces. On the other hand, the complexity of their multilayer application requires skilled labor and long time intervals for the production of work. To speed up the process of decorating the premises, an alternative option is used - plasterboard sheets.
Dry plaster
Finishing from sheets of building gypsum, lined on both sides with cardboard, can significantly reduce the time for finishing indoors, especially ceilings. All work consists in installing drywall with metal screws on special steel rails or on a wooden frame.
- On smooth walls or ceilings, such cladding can be glued with mastic containing gypsum and bone glue. After sealing joints between the sheets, you can proceed to the finish.
- Conventional drywall sheets (GCR) are not acceptable for exterior decoration. They are not used in wet and damp areas, as they can swell and exfoliate. For wet ones, moisture-resistant drywall (GKVL) is used, treated with a special solution in order to avoid mold and mildew from dampness. Where increased fire resistance is required, another type of drywall board is used - fire resistant (GKLO).
- Dry plaster makes it possible to create unusual in the form of partitions, niches, multi-level ceilings, podiums, imitations of fireplaces and much more.
Attention: There are various types of patterns on the plaster and it is better to make them a traditional material or textured material.
By type of plaster material is almost everything. Take a look at the photo and select the desired finishing material. On our site you can find material on the method of preparing any mixture.